22 Sep 2020
Hybrid Cloud With AWS Transit Gateway


Renjith Raju
#Technology | 4 Min Read
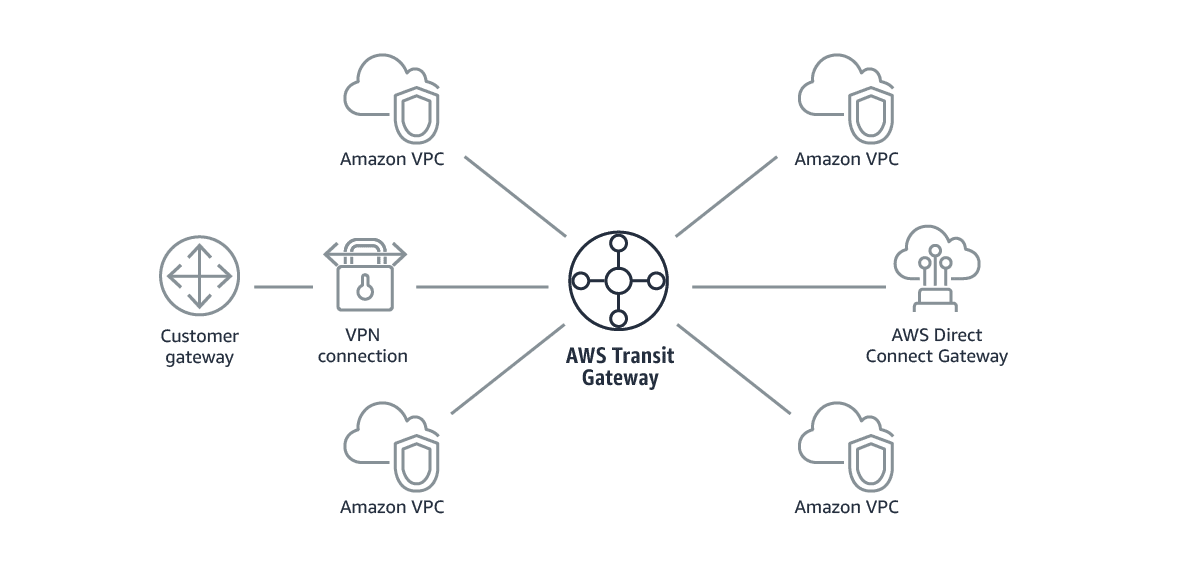
Transit Gateway is a highly available network gateway featured by Amazon Web Service. It eases the burden of managing connectivity between VPCs and from VPCs to On-premise data-center networks. This successfully allows organizations to build globally distributed networks and centralized network monitoring systems with minimal effort.
Earlier, the limitations with VPC Peering made it unable to create or connect VPN connections to On-premises networks directly. Also, to use transit VPC, a VPN Appliance had to be purchased from AWS Marketplace and connect all the VPCs to On-premise networks. This increased both the cost and maintenance.
Advantages of AWS Transit Gateway
- Transit Gateway is highly available and scalable.
- The best solution for hybrid cloud connectivity between On-premise and multiple cloud provider VPCs.
- It provides better security and efficiency to control traffic to various route tables.
- It helps to manage the AWS account routing globally.
- Manage AWS and On-premise network using a centralized dashboard.
- This helps to protect against distributed denial of service attacks and other common exploits.
Cost comparison between Transit Gateway vs VPC peering
| VPC Peering | Transit Gateway | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per VPC connection | None | $0.05/hour |
| Cost per GB transferred | $0.02 (0.01 charged to sender VPC owner and 0.01 charged to receiver VPC owner) | $0.02 |
| Overall monthly cost with 3 connected VPCs and 1 TB transferred | Connection charges – $0 Data Transfer Cost -$20 Total = $20/month |
Connection charges- $108 Data Transfer Cost – $20 Total = $128/month |
Transit gateway design best practices:
- Use a smaller CIDR subnet and use a separate subnet for each transit gateway VPC attachment.
- Based on the traffic, you can restrict NACLs rules.
- Limit the number of transit gateway route tables.
- Associate the same VPC route table with all of the subnets that are associated with the transit gateway.
- Create one network ACL and associate it with all of the subnets that are associated with the transit gateway. Keep the network ACL open in both the inbound and outbound directions.
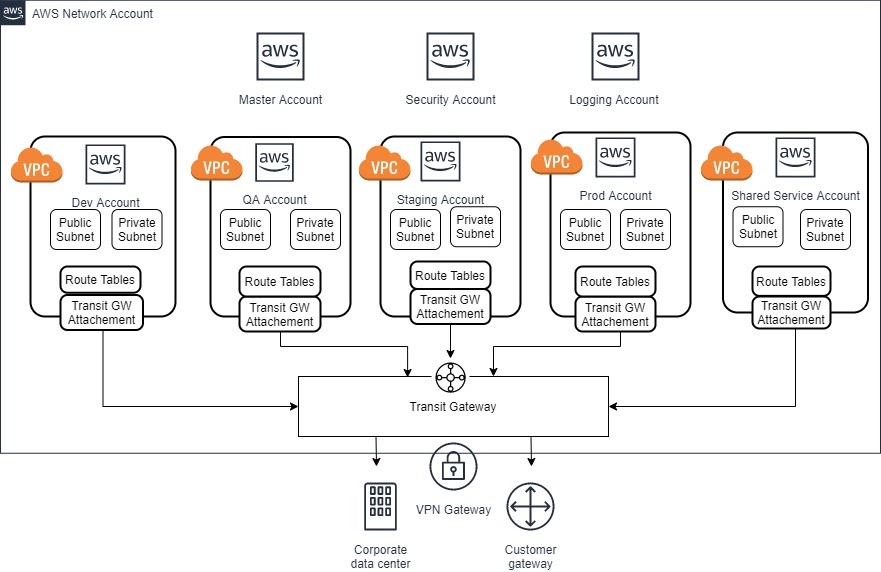
HashedIn, a cloud organization has a master billing account, logging, security, hosting networking infrastructure, a shared services account, three development, and one production level account for the architecture below. AWS Transit Gateway is the single point for all connectivity.
For each of the accounts, VPCs to Transit Gateway are connected via a Transit Gateway Attachment. Each account has a Transit Gateway Route Table, with an appropriate Gateway Attachment that sends traffic, and hence, subnet route tables can be used to connect from other networks. The Network account transit gateway is connected to the On-premise data center and other networks.
Here are the steps that are observed to configure multiple AWS accounts with AWS Transit Gateway:
- Firstly, access the AWS Console
- Up next, create the Transit Gateway
- Lastly, create Transit Gateway Attachment
- VPC
- VPN
- Peering Connection
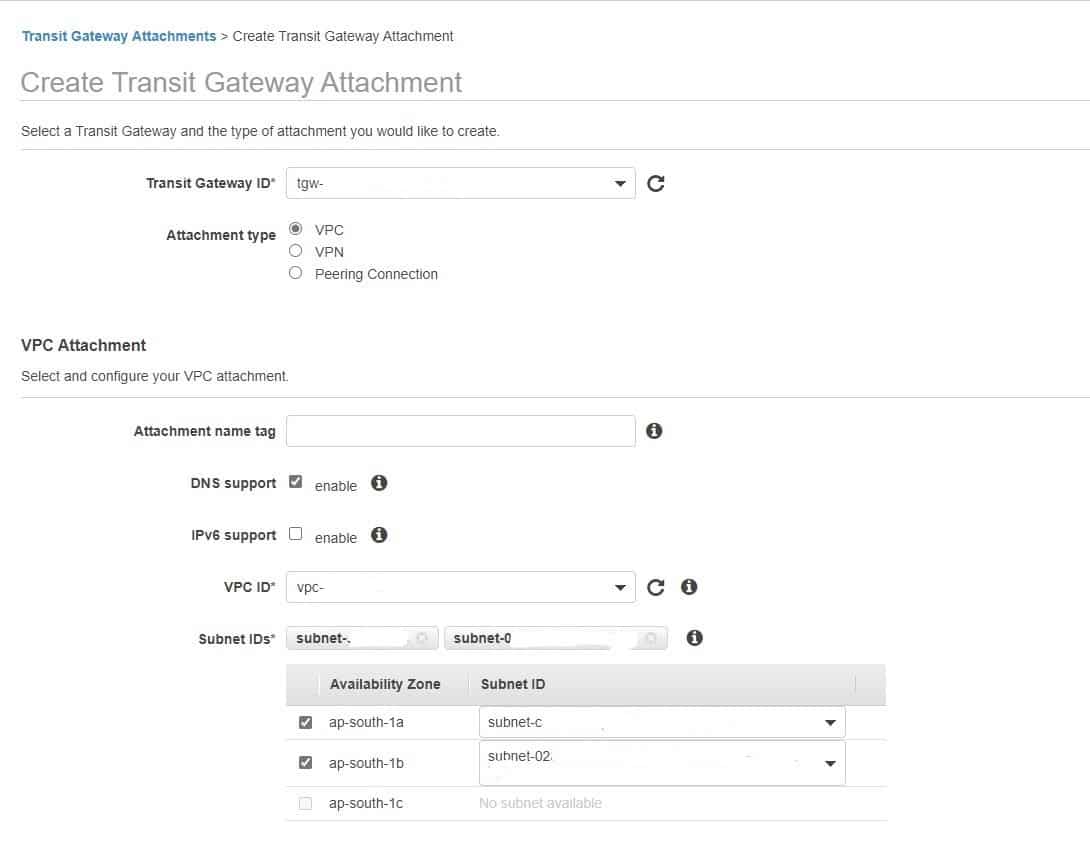
The three available options while creating Transit Gateway Attachment:
Using VPC, an ENI is created in multiple availability zones. A TGW attachment is needed to be developed in all availability zones in the VPC so that TGW can communicate with the ENI attachment in the same availability zone.
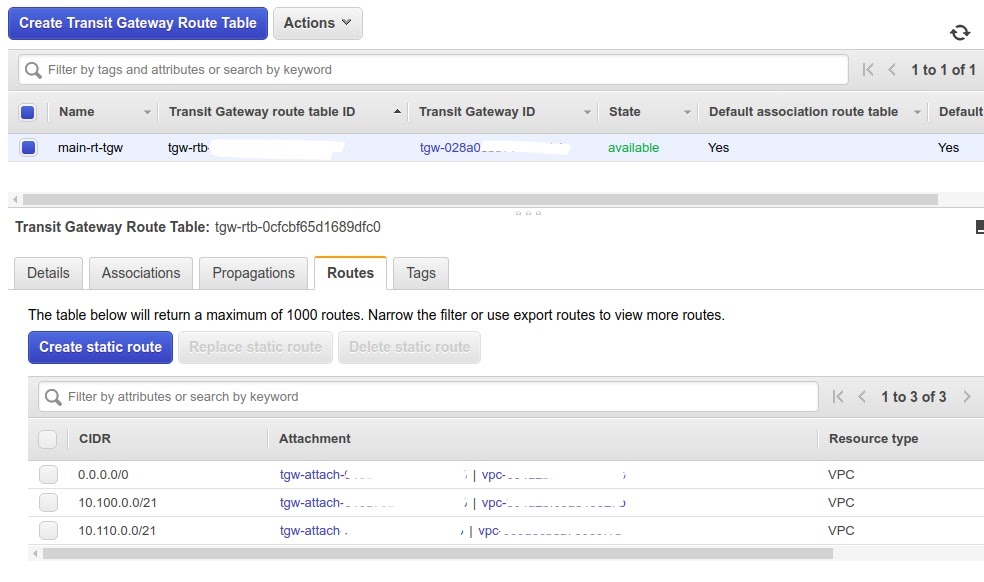
- Create Transit Gateway Route Table
- Add the routing rule for the respective TransitGateway ID
- Create an association and attach TransitGateway attachments
- Create static routes
Transit Gateway Attachments are associated with the Transit Gateway Route Table. However, you can create multiple attachments related to a single route table. Propagation will dynamically populate the routes of one attachment to a route table of another attachment. Associations help to attach Transit Gateway Attachments.
In addition, the network manager helps in reducing the operational complexity of connecting remote locations and other cloud resources. It also acts as a centralized dashboard to monitor the end-to-end networking operational activity in our AWS account.
Conclusion
The Transit Gateway is a centralized gateway where we can manage AWS and On-premise networks on a single dashboard. It also helps simplify network architecture, which was earlier complicated in managing inter-VPC connectivity and Direct Connect.